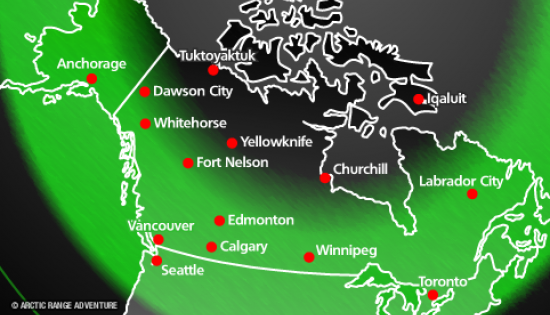
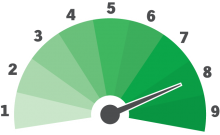
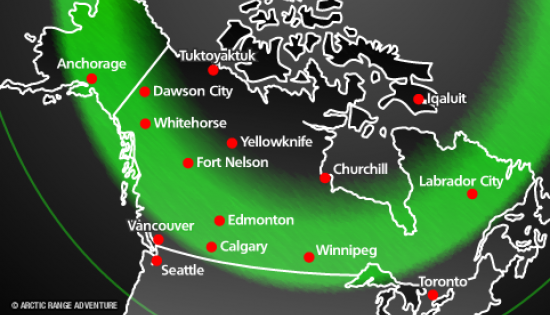
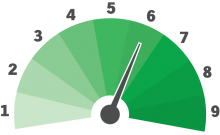
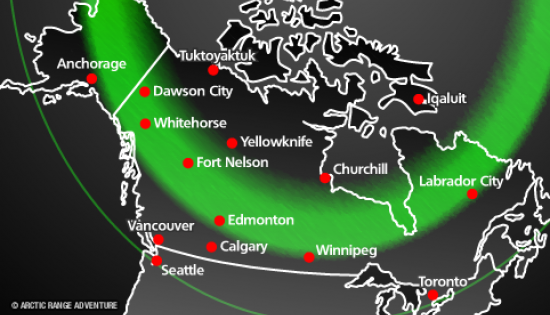
Anywhere from 10 minutes to all night long, depending on the magnitude of the incoming solar wind. "Coronal holes" consistently produce nice auroras but big solar flares and CMEs-coronal mass ejections are responsible for global-wide aurora displays…the BIG shows!
FAQ
How long do the northern lights last?
What is the aurora?
Aurora is a luminous glow of the upper atmosphere caused by energetic particles entering the atmosphere from above.
This definition differentiates aurora from other forms of airglow, and from sky brightness that is due to reflected or scattered sunlight. Airglow features that have "internal" energy sources are more common than aurora. For example, lightening and all associated optical emissions like sprites should not be considered aurora.
On Earth, the energetic particles that make aurora come from the geospace environment, the magnetosphere. These energetic particles are mostly electrons, but protons also make aurora. The electrons travel along magnetic field lines. The Earth's magnetic field looks like that of a dipole magnet where the field lines are coming out and going into the Earth near the poles. The auroral electrons are thus guided to the high latitude atmosphere near each pole. As the electrons penetrate into the upper atmosphere, the chance of colliding with an atom or molecule increases the deeper they go. Once a collision takes place, the atom or molecule takes some of the energy of the energetic particle and stores it as internal energy while the electron goes on at a reduced speed. The process of storing energy in a molecule or atom is called "exciting" the atom. An excited atom or molecule can return to the non-excited state (ground state) by sending off or emitting a photon, i.e. by making light.
Can I take Aurora photos with a cellphone?
Basically, it is very difficult to take night photos with a cellphone. To capture the Northern lights you will need to position your camera on a tripod to make sure you don't have any motion while you take a photo. We recommend to bring a camera which has a manual mode, which most medium-priced cameras have nowadays.
Three Day - Aurora Weather Forecast
Whitehorse (Canada)
Yukon Climate
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.0 (50) |
11.7 (53.1) |
16.8 (62.2) |
21.8 (71.2) |
34.1 (93.4) |
34.4 (93.9) |
33.2 (91.8) |
31.6 (88.9) |
26.7 (80.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
13.3 (55.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −11.0 (12.2) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
6.6 (43.9) |
13.5 (56.3) |
19.1 (66.4) |
20.6 (69.1) |
18.5 (65.3) |
12.1 (53.8) |
4.2 (39.6) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
5.1 (41.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −15.2 (4.6) |
−12.7 (9.1) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
1.0 (33.8) |
7.3 (45.1) |
12.3 (54.1) |
14.3 (57.7) |
12.6 (54.7) |
7.2 (45) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−12.5 (9.5) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −19.2 (−2.6) |
−17.6 (0.3) |
−11.9 (10.6) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
1.0 (33.8) |
5.6 (42.1) |
8.0 (46.4) |
6.7 (44.1) |
2.1 (35.8) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
−12.9 (8.8) |
−16.5 (2.3) |
−5.2 (22.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −56.1 (−69) |
−51.1 (−60) |
−42.2 (−44) |
−30.6 (−23.1) |
−12.9 (8.8) |
−6.1 (21) |
−2.2 (28) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−19.4 (−2.9) |
−31.1 (−24) |
−47.2 (−53) |
−48.3 (−54.9) |
−56.1 (−69) |
| Average mm (inches) | 17.8 (0.701) |
11.8 (0.465) |
10.3 (0.406) |
7.0 (0.276) |
16.3 (0.642) |
32.4 (1.276) |
38.1 (1.5) |
35.8 (1.409) |
33.3 (1.311) |
23.2 (0.913) |
20.1 (0.791) |
16.3 (0.642) |
262.3 (10.327) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.3 (0.012) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
1.2 (0.047) |
14.3 (0.563) |
32.4 (1.276) |
38.1 (1.5) |
35.5 (1.398) |
29.0 (1.142) |
8.8 (0.346) |
1.0 (0.039) |
0.4 (0.016) |
160.9 (6.335) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 25.4 (10) |
18.3 (7.2) |
14.8 (5.83) |
7.2 (2.83) |
2.0 (0.79) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.3 (0.12) |
4.7 (1.85) |
18.6 (7.32) |
27.0 (10.63) |
23.5 (9.25) |
141.8 (55.83) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 11.2 | 8.3 | 6.4 | 4.4 | 8.0 | 10.9 | 13.5 | 12.5 | 11.9 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.2 | 121.2 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 7.5 | 10.9 | 13.5 | 12.4 | 11.0 | 5.1 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 62.9 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 11.9 | 9.1 | 7.0 | 3.8 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 7.9 | 12.4 | 12.2 | 67.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 72.2 | 64.5 | 51.8 | 42.1 | 38.2 | 39.9 | 46.0 | 47.9 | 54.5 | 64.2 | 75.2 | 74.7 | 55.9 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 43.8 | 105.5 | 163.2 | 238.5 | 251.1 | 266.7 | 247.6 | 226.5 | 132.7 | 84.9 | 39.8 | 26.8 | 1,827.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 21.4 | 41.6 | 44.8 | 54.4 | 46.8 | 46.9 | 43.8 | 46.4 | 34.1 | 27.0 | 17.8 | 14.9 | 36.7 |